I. Bit to mask: (Magic Box fro Subnetting)
It is easy to write subnet mask in /8, /16...
What if you have to write in bit format or decimal format?
For that you have to just remember this Magic box (Bit to Mask Table).
So, we know:
/8 = 255.0.0.0
/16 = 255.255.0.0
/24 = 255.255.255.0
/32 = 255.255.255.255
What if we have /10, /27, /14...?
Using Magic Box,
/10 = /8 + /2 = 255.192.0.0 (2 is the number on the first row and take the value from below)
/27 = /24 + /3 = 255.255.255.224
/14 = /8 + /6 = 255.252.0.0
/21 = /16 + /5 = 255.255.248.0
soon on..
**Count from Left
For Wildmask just inverse the subnet mask
/27 = 0.0.0.31
/21 = 0.0.7.255
and soon on...
II. Host requirement are more
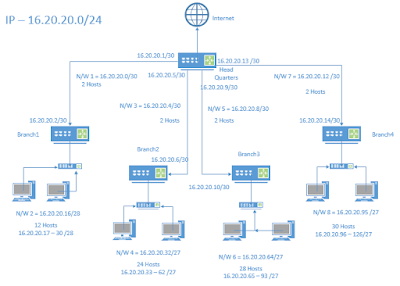
Example: 16.20.0.0/16, requirement 1000 hosts.
According to the host view of point subnetting,
 |
| Bit to Mask Table |
It is easy to write subnet mask in /8, /16...
What if you have to write in bit format or decimal format?
For that you have to just remember this Magic box (Bit to Mask Table).
So, we know:
/8 = 255.0.0.0
/16 = 255.255.0.0
/24 = 255.255.255.0
/32 = 255.255.255.255
What if we have /10, /27, /14...?
Using Magic Box,
/10 = /8 + /2 = 255.192.0.0 (2 is the number on the first row and take the value from below)
/27 = /24 + /3 = 255.255.255.224
/14 = /8 + /6 = 255.252.0.0
/21 = /16 + /5 = 255.255.248.0
soon on..
**Count from Left
For Wildmask just inverse the subnet mask
/27 = 0.0.0.31
/21 = 0.0.7.255
and soon on...
II. Host requirement are more
Example: 16.20.0.0/16, requirement 1000 hosts.
According to the host view of point subnetting,
- 1000+2 = 1002
- 2^10 = 1024, 10 bits on host side and 1024 numbers of host.
- 32-10 = 22 bits on network side
- 16.20.0.0/22
Now how you will divide into blocks,
- 1024/256 = 4, 256 (0 -255) is possible so we need 4 block of 256 (4X256)
Block 1: 16.20.0.0 - 16.20.3.255 /22
Block 2: 16.20.4.0 - 16.20.7.255 /22
.
.
.
.
Block last: 16.20.252.0 - 16.20.255.255 /22
★CT21
Reference: https://rstforum.net/ (CCNA training)